接雨水
11. Container With Most Water
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
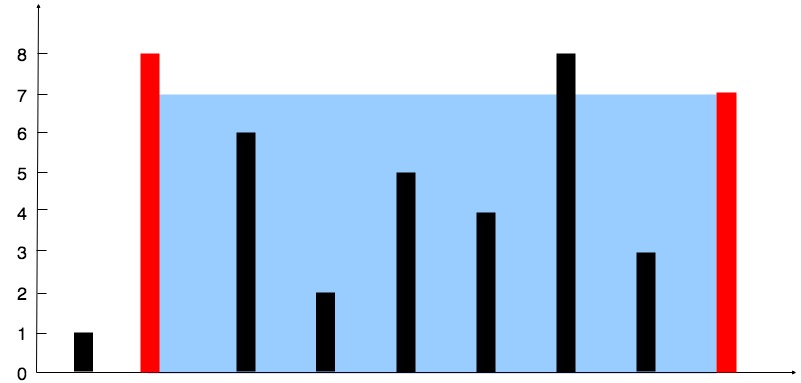
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1]
Output: 1
Constraints:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 10^50 <= height[i] <= 10^4
思路
双指针,左低移左,右低移右
The two-pointer technique starts with the widest container and moves the pointers inward based on the comparison of heights.
Increasing the width of the container can only lead to a larger area if the height of the new boundary is greater. By moving the pointers towards the center, we explore containers with the potential for greater areas.
C++ 解法
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int left = 0;
int right = height.size() - 1;
int maxArea = 0;
while (left < right) {
int currentArea = min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left);
maxArea = max(maxArea, currentArea);
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
};
Java 解法
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int result = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
while(left <= right){
result = Math.max(result, Math.min(height[right],height[left])*(right-left));
if(height[right] < height[left]) right--;
else left++;
}
return result;
}
}
Python 解法
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
left = 0
right = len(height) - 1
maxArea = 0
while left < right:
currentArea = min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left)
maxArea = max(maxArea, currentArea)
if height[left] < height[right]:
left += 1
else:
right -= 1
return maxArea
42. Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:

Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
Output: 9
Constraints:
n == height.length1 <= n <= 2 * 10^40 <= height[i] <= 10^5
思路
一共三种解法:双指针、单调栈和动态规划。
C++ 解法
单调栈
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
if(height.size() <= 2) return 0;
int result = 0;
stack<int> st;
st.push(0);
for(int i = 1; i < height.size(); i++){
if(height[i] < height[st.top()]){
st.push(i);
}else if(height[i] == height[st.top()]){
st.push(i);
}else{
while(!st.empty() && height[i] > height[st.top()]){
int mid = st.top();
st.pop();
if(!st.empty()){
int h = min(height[i], height[st.top()]) - height[mid];
int w = i - st.top() - 1;
result += h * w;
}
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return result;
}
};
Java 解法
双指针
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int i=0,left_max=height[0];
int sum=0;
int j=height.length-1,right_max=height[j];
while(i < j){
if(left_max <= right_max){
sum += left_max - height[i];
i++;
left_max = Math.max(left_max, height[i]);
}else{
sum += right_max - height[j];
j--;
right_max = Math.max(right_max, height[j]);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
Python 解法
双指针
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
i = 0
left_max = height[0]
sum = 0
j = len(height) - 1
right_max = height[j]
while i < j:
if left_max <= right_max:
sum += left_max - height[i]
i += 1
left_max = max(left_max, height[i])
else:
sum += right_max - height[j]
j -= 1
right_max = max(right_max, height[j])
return sum