二叉树深度高度节点数
- 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
- 111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
- 222. Count Complete Tree Nodes
- 110. Balanced Binary Tree
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10^4]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路
递归
C++解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
Java解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
Python3解法
Go解法
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Output: 5
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10^5]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
思路
递归
C++解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
if(root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL){
return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
}
if(root->right == NULL && root->left != NULL){
return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
}
return 1 + min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right));
}
};
Java解法
Python3解法
Go解法
222. Count Complete Tree Nodes
Given the root of a complete binary tree, return the number of the nodes in the tree.
According to Wikipedia, every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled in a complete binary tree, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2h nodes inclusive at the last level h.
Design an algorithm that runs in less than O(n) time complexity.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: 6
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5 * 10^4]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4- The tree is guaranteed to be complete.
思路
递归,从根节点出发统计的节点数=从根节点左节点出发统计的节点数+从根节点右节点出发统计的节点数+1
C++解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};
Java解法
Python3解法
Go解法
110. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
Example 1:
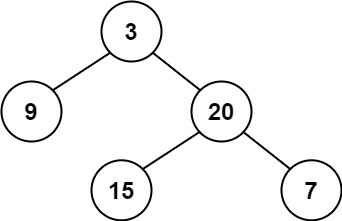
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: true
Example 2:
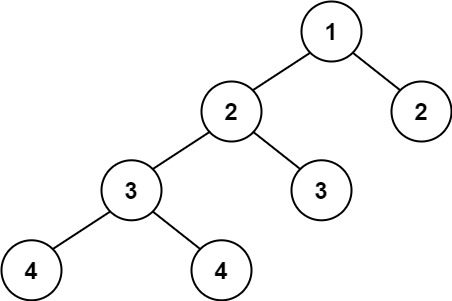
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: true
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
思路
递归
C++解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int getHeight(TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root->left);
if(leftHeight == -1){
return -1;
}
int rightHeight = getHeight(root->right);
if(rightHeight == -1){
return -1;
}
if(abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1){
return -1;
}else{
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}
};